Stronger SI Concepts
Unfolding social innovations' potential for smart and inclusive growth necessitates increasing their economic and social impact. This in turn, calls for their improvement for spread and growth. On the micro-level, the economic underpinning of a social innovation shapes its capacity, direction, impact and potential for scaling and diffusion. An overview of social innovation in Europe, however, suggests that it often takes the form of small initiatives generated by individuals, interest groups, creative communities, collaborating actors, and so on. SIMPACT's proposition is that these small, local social inventions and their working prototypes can be scaled-up, consolidated, replicated, and integrated with larger programs to generate large-scale sustainable transformation where favourable conditions are created by strategic actors.
SIMPACT will use «Design Thinking» to identify the economic enablers supporting social innovation to overcome the constraints of their own origins and settings to generate stronger and more widely distributed impacts. Addressing the strategic level, developing stronger social innovation concepts is expected to facilitate and resource new forms of entrepreneurship based on alternative business models of financing, distribution and employment.
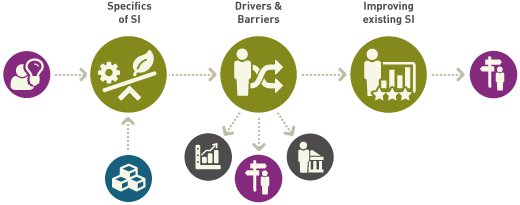
It comprises:
- Differentiating SI from other types of innovation learn more
- Identifying drivers and barriers of SI learn more
- Improving existing forms of SI learn more
Basic Information
-
Coordinator
POLIMI -
Contact
Alessandro DESERTI -
Involved Partners
IAT, TUDO, SIN, UM-MERIT, NORD, UEF -
Start date
06/2015
Glossary
- 1
Design Thinking
Design Thinking refers to the generation and implementation of new ideas about solving problems at the micro level and meeting one or more common goals by mainly focusing the process of design itself. In the context of social innovation a designarly approach is required to make initiatives more effective and replicable by reshaping and integrating objectives, forms of participation, the role of social drivers (versus that of technologies) and other external factors.