SI Meta Analysis
Background
The need to substantiate policy and practice by evidence is a yet emerging theme in social innovation. Although a growing body of examples of successful and less successful social innovations exists, these are rather scattered and documented in different ways, while covering a multiplicity of divers aspects.
Objective
Drawing from this rich but scattered evidence, meta-analysis will be applied to systematically summarise and integrate findings from existing social innovation case studies and analyse differences in the results, thus adding value to existing knowledge while avoiding duplication of research efforts.
Methodology
Striving for a qualitative collection of SI cases representing a variety of different settings in which social innovations emerge, develop and diffuse, a set of criteria will be applied for case selection. The following figure exemplifies related criteria.
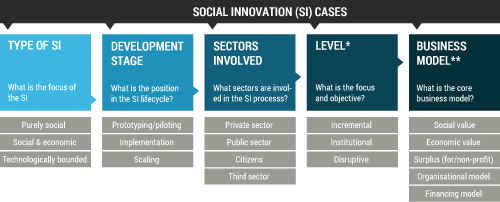
The focus will be on the economic factors derived from Go to WP1WP1 - Theorising considering the following aspects:
- 1problems to be solved, sectors and target groups;
- 2contexts (socio-economic, cultural, spatial, institutional context and welfare regimes);
- 3actors and stakeholders, considering implication for the users including gender aspects;
- 4processes, including the role played by ICTs and the collaboration between the different types of actors (public sector, private sector and third sector) and
- 5impacts, with emphasising how the different actors value the output of the social innovation.
Based on a multidimensional contextual approach, the meta-analysis will include:
- the analysis of underlying business and organisational models
- finance structures, distribution and employment aspects
- the identification of main actors, processes and outcomes of social innovation cases
- supporting infrastructures and applied indicators to measure social innovation impact
- gender-related specifics
The data analysis will be conducted by means of qualitative comparative analysis. The results will be summarised in a synthesis report and serve for a first review and evidence-based refinement of the SI classification/typology, the selection of cases for SI Go to WP3business case studies, Go to WP3social innovation biographies and Go to WP6policy cases, provide information on Go to WP5social innovation indicators and for the Go to WP2simulation iteration plus the development of Go to WP7evaluation methods.
Basic Information
-
Coordinator
NEOMA -
Contact
Sharam ALIJANI -
Involved Partners
IAT, UM-MERIT -
Start date
01/2014
Latest News

August 22, 2015
SIMPACT publishes its «Comparative Report on Social Innovation across Europe», which summarises the findings of 60 social innovation cases for which Business Case Studies and Social Innovation Biographies were conducted.

August 1, 2015
SIMPACT publishes the findings on meta-component, meta-objectives and meta-princripples across distinct welfare regimes derived from the meta-analysis of 94 social innovation cases collected from existing databases.
Glossary
- 1
Meta-Analysis
A systematic analysis in which the researcher compiles numerous previously published studies (here: social innovation cases) on a particular research question (e.g. economic principles, objectives and components) and re-analyses the results to find the general trend or patterns for results across the studies.
- 2
Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA)
QCA provides a bridge between qualitative and quantitative research, integrating features of «case-oriented» and «variable-oriented approaches». It conceptualises cases as combinations of attributes and uses Boolean algebra to derive simplified expressions of combinations that lead to a specific outcome.
- 3
Business Case Studies
A descriptive, exploratory or explanatory analysis of a case (e.g. business) to explore causation in order to identify underlying principles, objectives and components.
- 4
Social Innovation Biographies (SIB's)
SIB's allow for the reconstruction of social innovation from its idea to scaling and diffusion identifying involved actors, processes and networks as well as their interplay plus related economic principles, objectives and components appyling narrative interviewing methods and triangulation.